Commodity Production Costs Report
IPDI Production from Isophorone and Chlorine
IPDI Plant Capital & Operating Cost Analysis | United States | Q3 2025
This report presents the economics of Isophorone Diisocyanate (IPDI) production from isophorone and chlorine. The process examined is a typical phosgenation process. In the process examined, isophorone is reacted with hydrogen cyanide, generating isophorone nitrile (IPN). IPN obtained is then reacted with ammonia to form isophorone nitrile imine (IPNI), which is hydrogenated with more ammonia to yield isophorone diamine (IPDA). Finally, IPDA reacts with phosgene to produce IPDI. The phosgene used is generated from chlorine and carbon monoxid in an on-site unit.
The report provides a comprehensive study of IPDI production and related IPDI production cost, covering three key aspects: a complete description of the IPDI production process examined; an in-depth analysis of the related IPDI plant capital cost (Capex); and an evaluation of the respective IPDI plant operating costs (Opex).
The IPDI production process description includes a block flow diagram (BFD), an overview of the industrial site installations, detailing both the process unit and the necessary infrastructure, process consumption figures and comprehensive process flow diagrams (PFD). The IPDI plant capital cost analysis breaks down the Capex by plant cost (i.e., ISBL, OSBL and Contingency); owner's cost; working capital; and costs incurred during industrial plant commissioning and start-up. The IPDI plant operating costs analysis covers operating expenses, including variable costs like raw materials and utilities, and fixed costs such as maintenance, labor, and depreciation.
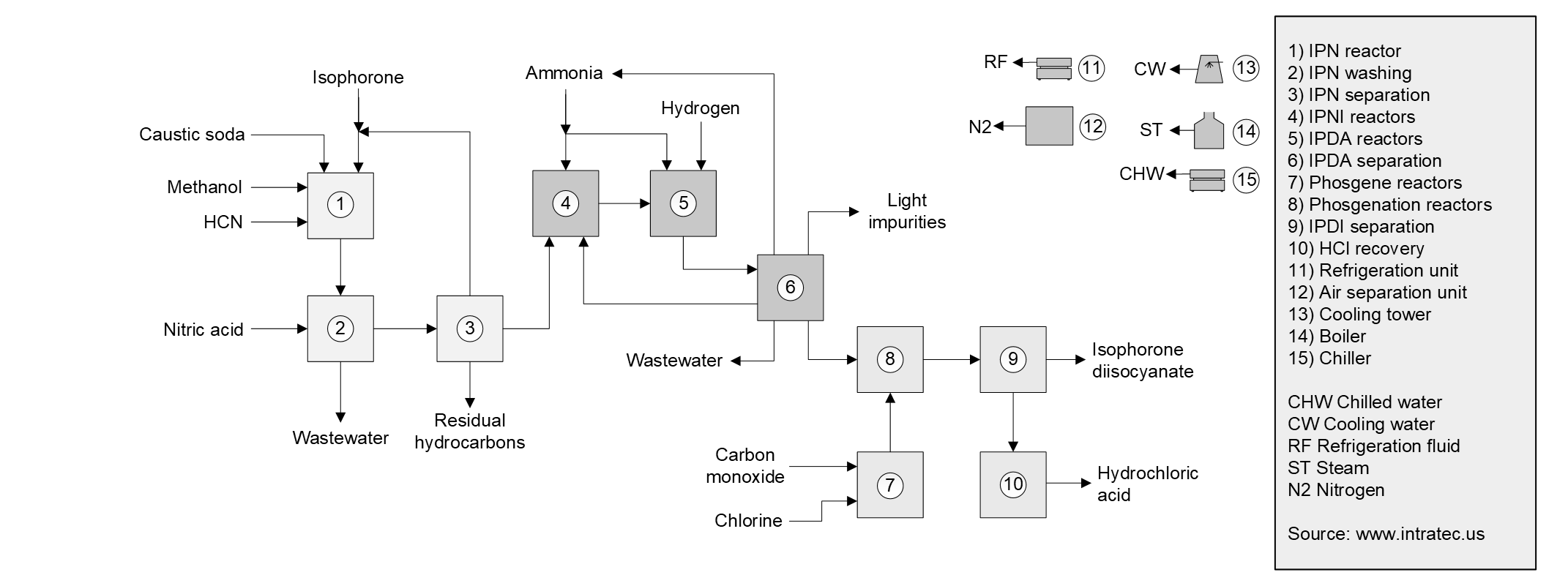
The process under analysis comprises three major sections: (1) Isophorone Hydrocyanation; (2) Isophorone nitrile (IPN) Amino-hydrogenation; and (3) Isophorone Diamine (IPDA) Phosgenation.
Isophorone Hydrocyanation. Initially, fresh and recycled isophorone are fed to a plug flow tubular reactor, along with hydrogen cyanide (HCN). The reaction is carried out in the presence of caustic soda, under atmospheric pressure. Excess of isophorone is used to avoid undesirable reactions (between HCN and the carbonyl group of isophorone). IPN is recovered from the hydrocyanation effluent after washing, distillation and evaporation steps. Caustic soda and unreacted isophorone are returned to the hydrocyanation.
IPN Amino-hydrogenation. The IPN obtained is mixed with excess ammonia and reacted to form isophorone nitrile imine (IPNI) in the presence of gamma-aluminum oxide catalyst. The product of the imination reaction, comprising IPNI, IPN and unreacted ammonia, is fed to the amino-hydrogenation reactors along with hydrogen and more ammonia. This reaction step occurs in the presence of conventional hydrogenation catalysts, yielding IPDA. Unreacted hydrogen and ammonia are separated from the amination effluent and recycled. The IPDA-rich stream is subsequently submitted to distillation and evaporation steps for purification.
IPDA Phosgenation. IPDA and phosgene are vaporized and superheated, then they are fed to the reactors.The mixture is kept at high temperatures for a short time in order to avoid the generation of side products or the decomposition of phosgene. Solvent is used to condense the isophorone diisocianate formed. The liquid stream is further treated to remove the solvent, as well as light and heavy ends. Finally, the purified IPDI product is obtained. The gaseous effluent obtained after liquefaction of IPDI is further treated, in order to recover phosgene and hydrogen chloride.
Report in PDF Format
Download & Explore Anytime
Access in Various Devices
Print & Read Comfortably
Share With Co-workers
Up-to-date Report
Professional report based on Q3 2025 economic data, ensuring timely evaluations.
Multiple Use Cases
Ideal for investment screening, feasibility studies, cost estimates, and research planning.
Proven Methodology
Developed using a consistent methodology honed over a decade, ensuring reliable cost analyses.
Report Editions
Content Highlights
Plant Capital Cost Summary
Summary outlining the capital cost required for building the IPDI production plant examined.
Plant Capital Cost Details
Detailing of fixed capital (ISBL, OSBL & Owner’s Cost), working capital and additional capital requirements.
Plant Cost Breakdowns
Breakdown of IPDI process unit (ISBL) costs and infrastructure (OSBL) costs; plant cost breakdown per discipline.
Operating Costs Summary
Summary presenting the operating variable costs and the total operating cost of the IPDI production plant studied.
Operating Cost Details
Detailing of utilities costs, operating fixed costs and depreciation.
Plant Capacity Assessment
Comparative analysis of capital investment and operating costs for different IPDI plant capacities.
Production Process Information
Block Flow Diagram, descriptions of process unit (ISBL) and site infrastructure (OSBL).
Process Consumptions
Raw materials and utilities consumption figures, by-products credits, labor requirements
Process Diagrams
Process flow diagrams (PFD), equipment list and industrial site configuration
Other IPDI Production Cost Reports

IPDI Production from Isophorone and Urea
This study examines the economics of Isophorone Diisocyanate (IPDI) production from isophorone and urea in the United States. This process is a non-phosgene route. In the non-phosgene process, IPDA reacts with urea and butanol generating a carbamate intermediate. Then, the carbamate is thermally cracked producing IPDI.
Details: 15 kta United States-based plant | Q3 2025 | 107 pages | Issue B | From $799 USD
Bundle & Save
Purchase multiple IPDI Production Cost reports and enjoy tiered discounts
up to 10% off!
Could Not Find the Report You Need?
Obtain a Bespoke Report
Get a report targeting the process in which you are interested
See Offer Details
Understand Bespoke Reports and how you can easily order them
Check Editions & Pricing
Complete a brief form and see a quotation for your Bespoke Report
Other Related Production Cost Reports

Chlorine Production from Sodium Chloride (Diaphragm Process)
This study presents the economics of Chlorine production from sodium chloride via a diaphragm plant located in the United States. In the process under analysis, an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine) is decomposed electrolytically in a diaphragm cell, producing Chlorine, sodium hydroxide and hydrogen.
Details: 550 kta United States-based plant | Q3 2025 | 107 pages | Issue B | From $799 USD

Ammonia Production from Natural Gas (Combined Reforming)
This report presents the economics of Ammonia production from natural gas in the United States using a process similar to KBR Purifier process. In the process examined, syngas is initially produced from natural gas via a combined reforming. The syngas is purified through several steps into nitrogen and hydrogen which are synthesized to ammonia.
Details: 800 kta United States-based plant | Q3 2025 | 107 pages | Issue B | From $1,199 USD

Hydrogen Cyanide from Ammonia and Natural Gas (Without Air)
This report provides the economics of Hydrogen Cyanide production in the United States using a direct synthesis method similar to BMA (Blausäure-Methan-Ammoniak) process, which involves the reaction of ammonia and methane (natural gas) without air.
Details: 60 kta United States-based plant | Q3 2025 | 107 pages | Issue B | From $799 USD

Chlorine Production from Sodium Chloride (Membrane Process)
This study presents the economics of Chlorine production from sodium chloride via a membrane process plant located in the United States. In the process under analysis, an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine) is decomposed electrolytically in a membrane cell, producing Chlorine, sodium hydroxide and hydrogen.
Details: 500 kta United States-based plant | Q3 2025 | 107 pages | Issue A | From $799 USD

Hydrogen Cyanide from Ammonia and Natural Gas (With Air)
This study provides the economics of Hydrogen Cyanide production in the United States using a direct synthesis method similar to Andrussow process, which involves the reaction of ammonia, methane (natural gas), and air to produce HCN.
Details: 100 kta United States-based plant | Q3 2025 | 107 pages | Issue A | From $799 USD

Ammonia Production from Syngas
This report presents the economics of Ammonia production from synthesis gas (syngas). In this process, hydrogen, recovered from syngas feedstock, and nitrogen, recovered from air, react producing Ammonia. The economic analysis performed assumes a plant located in the United States.
Details: 800 kta United States-based plant | Q3 2025 | 107 pages | Issue A | From $799 USD

Carbon Monoxide Production
This report presents the economics of a typical cryogenic partial condensation process for Carbon Monoxide (CO) production from synthesis gas (syngas) in the United States. In this process, CO and hydrogen from syngas are separated in heat exchangers at cryogenic temperatures.
Details: 300 kta United States-based plant | Q3 2025 | 107 pages | Issue A | From $799 USD
+800 Reports Developed, Targeting +250 Commodities
Vast Report Library
858 independent and up-to-date reports examining embryonic and established production processes.
Free Sample Reports
Quickly understand the structure and depth of content of our professional reports.

