Commodity Production Costs Report
Butyraldehyde from Propylene and Syngas (N/Iso Ratio of 30:1)
Butyraldehyde Plant Capital & Operating Cost Analysis | United States | Q4 2025
This report presents the economics of n-Butyraldehyde production from propylene and syngas. The process examined is similar to the LP OXO technology, jointly licensed by JM Davy and Dow, using Selector 30 catalyst and employing the liquid recycle concept for product recovery. In this process, the production ratio of n- to iso-butyraldehyde in the oxo reaction is about 30. The n-Butyraldehyde is separated as the final product and the isobutyraldehyde is obtained as a by-product.
The report provides a comprehensive study of Butyraldehyde production and related Butyraldehyde production cost, covering three key aspects: a complete description of the Butyraldehyde production process examined; an in-depth analysis of the related Butyraldehyde plant capital cost (Capex); and an evaluation of the respective Butyraldehyde plant operating costs (Opex).
The Butyraldehyde production process description includes a block flow diagram (BFD), an overview of the industrial site installations, detailing both the process unit and the necessary infrastructure, process consumption figures and comprehensive process flow diagrams (PFD). The Butyraldehyde plant capital cost analysis breaks down the Capex by plant cost (i.e., ISBL, OSBL and Contingency); owner's cost; working capital; and costs incurred during industrial plant commissioning and start-up. The Butyraldehyde plant operating costs analysis covers operating expenses, including variable costs like raw materials and utilities, and fixed costs such as maintenance, labor, and depreciation.
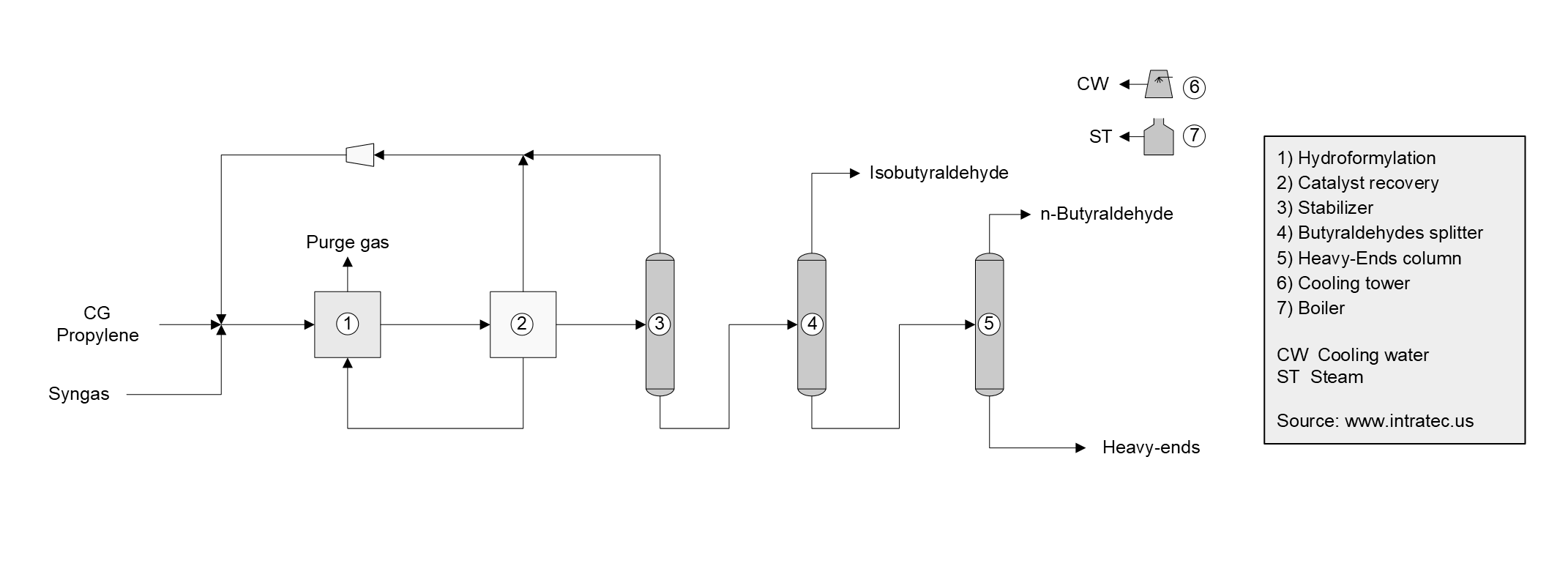
The process under analysis comprises the following major sections: (1) hydroformylation; (2) catalyst recovery and (3) purification.
* Hydroformylation. Fresh propylene and syngas are treated to remove impurities that could poison the rhodium catalyst employed in the hydroformylation reaction. The purified raw materials, recycled reactants and recycled catalyst solution are fed to the first of two reactors operating in series. In both reactors, the propylene reacts with carbon monoxide and hydrogen at mild temperatures and low pressures, and in the presence of a homogeneous rhodium-based catalyst with an organophosphite ligand, yielding n-Butyraldehyde as main product and isobutyraldehyde by-product. The catalyst is dissolved in the high-boiling reaction by-products.
* Catalyst recovery. The liquid effluent from the hydroformylation, containing catalyst components, reaction products, unreacted propylene, as well as aldehyde products with some dissolved gases, is depressurized and fed to a falling-film evaporator. The concentrated catalyst solution obtained from evaporator is recycled to the hydroformylation area, with a small portion directed to a catalyst regeneration step. The vapor from evaporator is partially condensed and the uncondensed gas is recycled to the reactor through a compressor. The condensed liquid stream is sent to the purification steps.
* Purification. The condensed liquid stream containing the aldehydes from the catalyst recovery is directed to the first of three distillation columns for the purification of n-Butyraldehyde product. In the first column, the stabilizer column, remaining traces of dissolved gases are removed (propylene, propane, and other inert gases) and recycled to the hydroformylation. The bottom stream from the stabilizer column is fed to a second distillation column, where isobutyraldehyde is separated. In the third column, the heavy-ends column, heavies impurities are separated from the n-Butyraldehyde product (with 99 wt% purity), which is finally routed to storage facilities located outside battery limits.
Report in PDF Format
Download & Explore Anytime
Access in Various Devices
Print & Read Comfortably
Share With Co-workers
Up-to-date Report
Professional report based on Q4 2025 economic data, ensuring timely evaluations.
Multiple Use Cases
Ideal for investment screening, feasibility studies, cost estimates, and research planning.
Proven Methodology
Developed using a consistent methodology honed over a decade, ensuring reliable cost analyses.
Report Editions
Content Highlights
Plant Capital Cost Summary
Summary outlining the capital cost required for building the Butyraldehyde production plant examined.
Plant Capital Cost Details
Detailing of fixed capital (ISBL, OSBL & Owner’s Cost), working capital and additional capital requirements.
Plant Cost Breakdowns
Breakdown of Butyraldehyde process unit (ISBL) costs and infrastructure (OSBL) costs; plant cost breakdown per discipline.
Operating Costs Summary
Summary presenting the operating variable costs and the total operating cost of the Butyraldehyde production plant studied.
Operating Cost Details
Detailing of utilities costs, operating fixed costs and depreciation.
Plant Capacity Assessment
Comparative analysis of capital investment and operating costs for different Butyraldehyde plant capacities.
Production Process Information
Block Flow Diagram, descriptions of process unit (ISBL) and site infrastructure (OSBL).
Process Consumptions
Raw materials and utilities consumption figures, by-products credits, labor requirements
Process Diagrams
Process flow diagrams (PFD), equipment list and industrial site configuration
Other Butyraldehyde Production Cost Reports

Butyraldehyde from Propylene and Syngas (N/Iso Ratio of 10:1)
This feasibility study approaches n-Butyraldehyde production from propylene and syngas, assuming a plant located in the United States. The process under analysis is a propylene hydroformylation similar to the LP OXO technology jointly developed by JM Davy and Union Carbide, employing Selector 10 catalyst. The production ratio of n- to iso-butyraldehyde is about 10.
Details: 160 kta United States-based plant | Q4 2025 | 107 pages | Issue B | From $799 USD

Butyraldehyde from Propylene and Syngas (N/Iso Ratio of 4:1)
This report concerns the costs associated with the production of n-Butyraldehyde from propylene and syngas. The process under analysis is a propylene hydroformylation similar to the technology jointly developed by Rhodia (former Rhône-Poulenc) and Ruhrchemie. The economic analysis presented assumes a plant located in the United States.
Details: 160 kta United States-based plant | Q4 2025 | 107 pages | Issue C | From $799 USD
Bundle & Save
Purchase multiple Butyraldehyde Production Cost reports and enjoy tiered discounts
up to 20% off!
Could Not Find the Report You Need?
Obtain a Bespoke Report
Get a report targeting the process in which you are interested
See Offer Details
Understand Bespoke Reports and how you can easily order them
Check Editions & Pricing
Complete a brief form and see a quotation for your Bespoke Report
Other Related Production Cost Reports

Trimethylolpropane Production
This report presents the economics of Trimethylolpropane (TMP) production from formaldehyde and n-butyraldehyde, assuming a plant located in the United States. In the process analyzed, formaldehyde and n-butyraldehyde go through an aldol condensation and a cross-Cannizaro reaction to form Trimethylolpropane, using 2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)butanal as intermediate.
Details: 20 kta United States-based plant | Q4 2025 | 107 pages | Issue A | From $1,199 USD

2-Ethylhexanoic Acid Production from Butyraldehyde
This report presents the economics of 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid production from Butyraldehyde in the United States. In this process, n-butyraldehyde undergoes an aldol condensation reaction yielding 2-ethylhexenal, which is then hydrogenated to form 2-ethylhexanal. The aldehyde is subsequently subjected to an oxidation reaction to produce the 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid.
Details: 60 kta United States-based plant | Q4 2025 | 107 pages | Issue A | From $1,999 USD
+800 Reports Developed, Targeting +250 Commodities
Vast Report Library
858 independent and up-to-date reports examining embryonic and established production processes.
Free Sample Reports
Quickly understand the structure and depth of content of our professional reports.

